How is a high-precision image measuring instrument applied to the measurement of precision parts?
In the field of precision manufacturing, the dimensional accuracy and geometric consistency of components directly impact product performance and reliability. From micron-level tolerance control in aerospace components to millimeter-level assembly matching in automotive parts, and down to nanometer-level surface quality inspection in electronic components, high-precision measurement has become a core element in ensuring product quality.


Traditional measuring tools (such as calipers, micrometers, and projectors) can meet basic requirements, but they often suffer from low efficiency, insufficient accuracy, and complex operation when dealing with complex geometries, minute dimensions, or non-contact inspection scenarios. High-precision image measuring instruments, with their advantages of non-contact measurement, high-resolution imaging, and intelligent software analysis, are emerging as the mainstream solution for precision part inspection.


I. Core Technical Principles of High-Precision Image Measuring Instruments

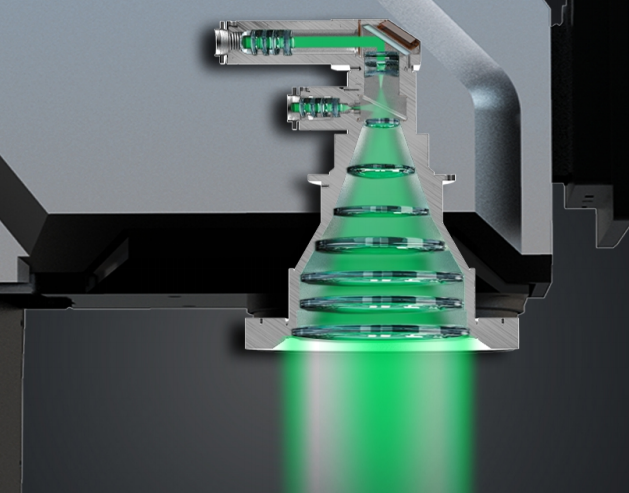
The core of the high-precision image measuring instrument lies in the deep integration of its optical imaging system and intelligent measurement software. Its working principle can be broken down into the following steps:
1. High-Resolution Optical Imaging System
- Industrial Camera: Equipped with high-resolution CCD or CMOS sensors to capture micron-level details on part surfaces;
- Telecentric Lens: Eliminates perspective distortion, ensuring sharp image edges for measuring flat parts;
- Multi-Lighting System: Combines ring lights, coaxial lights, and backlights to adapt to diverse materials and surface characteristics (e.g., reflective, transparent, textured surfaces);
- Magnification: Supports 0.5X-10X continuous zoom, covering measurement needs from macro overviews to microscopic details.
2. Smart Measurement Software
- Edge Detection Algorithm: Automatically identifies over 20 geometric elements including straight lines, circles, arcs, and ellipses, with manual correction support;
- Dimension Annotation Function: One-click measurement of key parameters such as length, diameter, angle, and spacing to generate inspection reports;
- CAD Comparison Module: Import design drawings to compare actual parts against theoretical models in real time, annotating out-of-tolerance areas;
- SPC Statistical Analysis: Records historical data, generates trend charts and CPK values to assist production process control.
II. Four Major Application Scenarios for High-Precision Image Measurement Instruments

1. Edge Measurement: Ensuring Part Contour Accuracy
- Application Scenario: Contour dimension inspection of parts such as sealing rings, O-rings, gaskets, etc.
2. Bore Measurement: Controlling Assembly Clearance and Go/No-Go Gauges
- Application Scenarios: Inspection of PCB through-holes, threaded holes in mechanical components, engine cylinder bores, etc.
3. Groove Measurement: Evaluating Surface Finish Quality
- Application Scenarios: Depth and width inspection of bearing raceways, gear tooth cavities, mold cavities, etc.
4. Complex Geometric Shape Measurement: Comprehensive Quality Control
- Application Scenarios: Inspection of non-standard parts such as turbine blades, irregular springs, and curved casings.
III. Three Major Advantages of High-Precision Image Measuring Instruments


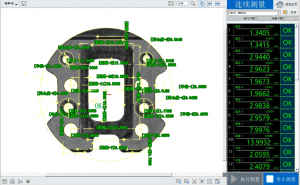



1. Non-contact measurement: Protecting precision surfaces
- Avoid contact measurements (such as calipers or coordinate measuring machine stylus tips) that may scratch part surfaces;
- Applicable materials: metals, plastics, ceramics, glass, rubber, etc.;
- Particularly suitable for inspecting high-surface-finish parts (such as optical lenses and semiconductor wafers).
2. High-efficiency batch inspection: Boosting production cycle time
- Single imaging session can simultaneously measure multiple features (e.g., 50 apertures on a single circuit board);
- Supports programmable automated measurement with new part import time ≤30 minutes;
- Integrates with automated production lines to achieve closed-loop control of “inspection-sorting-feedback.”
3. Data-Driven Decision Making: Optimizing Production Processes
- Measurement data is automatically stored and supports SPC statistical analysis;
- Evaluates production process stability through CPK values to provide early warnings of quality risks;
- Provides data-driven insights for process improvements (e.g., adjusting grinding parameters, optimizing mold design).
Product recommendation
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
MORE+You may also be interested in the following information
FREE CONSULTING SERVICE
Let’s help you to find the right solution for your project!


 ASK POMEAS
ASK POMEAS  PRICE INQUIRY
PRICE INQUIRY  REQUEST DEMO/TEST
REQUEST DEMO/TEST  FREE TRIAL UNIT
FREE TRIAL UNIT  ACCURATE SELECTION
ACCURATE SELECTION  ADDRESS
ADDRESS Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
