In semiconductor, medical equipment, precision machinery and other fields, the dimensional accuracy of tiny machined parts has entered the micron or even nano-scale era. Traditional inspection technology is difficult to meet the demand due to lens distortion, parallax error and other problems, and telecentric lens, with its unique optical design, has become a key tool to break through the bottleneck of sub-micron inspection.


Telecentric Lenses: An Optical Revolution to Eliminate Parallax
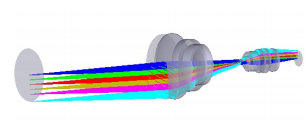
Telecentric lens through the parallel optical path design, so that the main light ray is always parallel to the optical axis, fundamentally solving the traditional lens due to perspective effect caused by the near large and far small aberration problem.
Advantage 1: Zero parallax measurement: changes in object distance do not affect the imaging size, to ensure the accurate measurement of small features (such as 0.1μm line width);
Advantage 2: High depth of field coverage: in high magnification still maintains a clear image, compatible with the detection of complex three-dimensional structures;
Advantage 3: Low aberration rate: through the aspheric lens and precision coating technology, the geometric aberration will be controlled to 0.01% or less.
Micromachined parts inspection applications
1. Semiconductors and electronic components: chip, PCB and other components of the dimensional accuracy and defect control directly affect product performance:
-
Weld ball inspection: Measure the height and coplanarity of the weld ball within an error of ±1μm;
-
Line analysis: Identifies 0.01mm line width deviations and copper bumps, supporting high-density package inspection.


2. Medical Precision Devices: The processing precision of medical devices such as microcatheters and microfluidic chips is a matter of patient safety:
-
Catheter Tip Measurement: Analyzes bevel angle and opening diameter for ultra-fine catheters up to 0.1mm;
-
Microchannel Inspection: Verify channel size and surface roughness to ensure liquid flow stability.


3. Precision machinery and aerospace: parts such as micro gears, turbine blades, etc. need to meet both dimensional and geometric tolerances:
-
Micro Gear Measurement: Tooth shape and pitch accuracy of ±2μm, supporting gears with module 0.1mm or less;
-
Coating Inspection: Identifying thermal barrier coating defects to safeguard aero-engine reliability.


Technology Evolution: From Passive Imaging to Intelligent Sensing
1. Multi-spectral fusion: combining visible and infrared light to penetrate the surface of the material to detect internal defects;
2. Dynamic compensation system: adapting to complex workshop environments through temperature compensation and auto-focusing;
3. AI synergistic algorithms: analyzing the image features in real time to automate defect classification and data tracing.
Industry Case: Improving Inspection Efficiency and Accuracy in Practice
1. Efficiency Improvement: 4 times faster single-station inspection speed, 30% increase in annual production capacity;
2. Accuracy Breakthrough: Reduced dimensional measurement error from ±3μm to ±0.8μm, 2.5% increase in yield;
3. Cost Optimization: Reduced manual intervention and rework costs, 40% reduction in overall costs.
Product recommendation
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
MORE+You may also be interested in the following information
FREE CONSULTING SERVICE
Let’s help you to find the right solution for your project!


 ASK POMEAS
ASK POMEAS  PRICE INQUIRY
PRICE INQUIRY  REQUEST DEMO/TEST
REQUEST DEMO/TEST  FREE TRIAL UNIT
FREE TRIAL UNIT  ACCURATE SELECTION
ACCURATE SELECTION  ADDRESS
ADDRESS Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
