In the wave of intelligent manufacturing and industrial automation, line laser sensors are becoming one of the core technologies in the field of machine vision inspection. By emitting laser light and capturing reflected signals, this seemingly ordinary optical device can quickly and accurately acquire three-dimensional contour information on the surface of an object, providing a revolutionary solution for quality control, dimensional measurement and defect detection in industrial production.
Principle of operation of line laser sensors
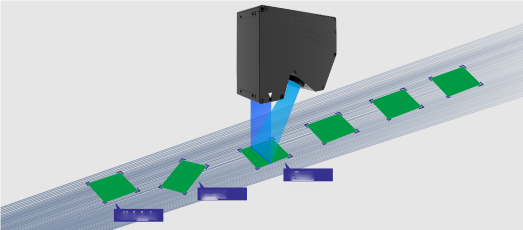
Line laser sensors are based on the principle of triangulation by emitting a laser line (usually a red or blue laser) to the surface of the object to be measured and receiving the reflected light using a highly sensitive camera. Due to the angle between the laser line and the camera lens, changes in the height of the object's surface cause the position of the reflected spot to shift on the camera sensor. By calculating the change in spot position, the sensor reconstructs a 3D profile of the object.
This non-contact measurement method is characterized by high accuracy (micron level), high speed (millisecond response) and strong resistance to environmental interference, which is especially suitable for real-time inspection needs in complex industrial environments.
Core applications in machine vision inspection
1. 3D Contour Measurement and Dimensional Inspection
In automotive manufacturing, electronic component processing and other fields, the three-dimensional dimensional accuracy of products directly affects performance and assembly quality. Line laser sensors can quickly scan complex structures such as curved surfaces, holes, edges, etc. and generate high-density point cloud data. For example:
① automotive parts inspection: measuring the flatness of the engine block, gearbox gear tooth shape error;
② Electronic chip inspection: to detect the height of the pads of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and the coplanarity of BGA packages.


2. Highly accurate positioning and alignment
In automated production lines, robots or robotic arms need to accurately grasp or place workpieces. Line laser sensors can acquire the position and attitude information of the object in real time and guide the equipment to complete high-precision alignment. Example:
① Photovoltaic module production: locate the cutting position of the cell;
① PV module production: locating the cutting position of the cell sheet; ② Logistics sorting: recognizing the placing angle of the parcel and adjusting the movement of the robotic arm.

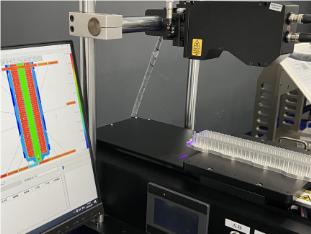
3. Defect detection and surface analysis
Surface defects (e.g. scratches, dents, cracks) in industrial products can affect service life. Line laser sensors can quickly identify imperfections that are difficult to detect with the naked eye by analyzing the intensity and distribution of reflected light. Examples:
① Metal sheet inspection: detect surface bumps or pits on cold rolled steel sheets;
② Food packaging inspection: checking the flatness or sealing integrity of glass bottles.


4. Dynamic monitoring and process control
On high-speed production lines, line laser sensors enable dynamic real-time monitoring. For example:
① Injection molding monitoring: detect the wall thickness uniformity of plastic parts;
② Pipe production monitoring: online measurement of pipe diameter and ovality.
Line laser sensors are moving towards higher accuracy, smaller size and multi-sensor fusion.
Product recommendation
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
MORE+You may also be interested in the following information
FREE CONSULTING SERVICE
Let’s help you to find the right solution for your project!


 ASK POMEAS
ASK POMEAS  PRICE INQUIRY
PRICE INQUIRY  REQUEST DEMO/TEST
REQUEST DEMO/TEST  FREE TRIAL UNIT
FREE TRIAL UNIT  ACCURATE SELECTION
ACCURATE SELECTION  ADDRESS
ADDRESS Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
