How does the depth of field of industrial lenses affect inspection?
In the field of industrial inspection, the industrial lens is a key component for acquiring image information, and its performance has a crucial impact on the inspection results. And the depth of field as an important parameter of the industrial lens, profoundly affecting the detection effect. So, how exactly does the depth of field of industrial lenses affect the detection effect?
The concept of depth of field
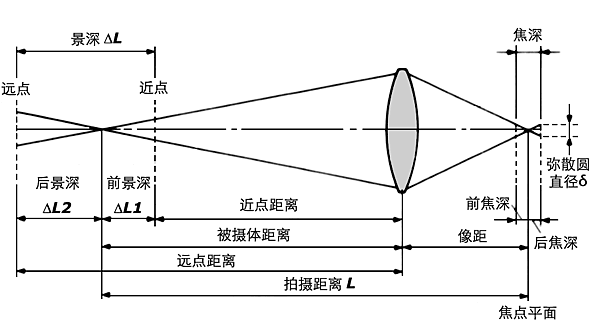

Depth of field, in simple terms, refers to the distance range before and after the focus of the lens focus is completed, the focus can present a clear image. When the lens focuses on an object, the object before and after a certain distance within a certain distance of other objects, but also in the imaging plane to form a relatively clear image, the depth of space of this clear image is the depth of field. For example, in the shooting of a product photo, in addition to our focus on the product surface of a characteristic point, before and after a certain range of surface details can also be clearly imaged, this range is the depth of field.
Impact of Large Depth of Field on Detection Effectiveness

(i) Advantages
1. Full inspection: A large depth of field enables a larger range of objects to be clearly imaged at the same time. In industrial inspection, this means that more parts of the object to be tested can be detected at once, whether it is the surface of the different height areas, or the same plane in different locations on the features, can be clearly presented in the image, without the need to frequently adjust the lens focus. For example, in the detection of circuit boards, a large depth of field lens can be clearly presented at the same time on the circuit board at different heights of the electronic components as well as the line, so that inspectors can comprehensively check the circuit board soldering quality, line connectivity and other issues.
2. Reduce the focusing accuracy requirements: due to the greater depth of field, the lens focusing accuracy requirements are relatively low. In some of the production environment is not stable, the position of the test object has some fluctuations in the case, the large depth of field lens can still ensure that the detection of the region's clear imaging, to reduce the focus deviation caused by the detection of errors. For example, in the assembly line on the irregularly shaped parts inspection, the position of the parts may be slightly shifted, the large depth of field lens can adapt to this change, to ensure the accuracy of detection.
(ii) Limitations
1. Relatively lower resolution: Large depth-of-field lenses often require some optical design to extend the depth-of-field range, which may sacrifice image resolution to some extent. When detecting tiny defects or high-precision dimensional measurements, the lower resolution may not be able to meet the inspection requirements, resulting in some subtle defects being difficult to detect. For example, for detecting nanoscale scratches on the surface of a chip, a large depth-of-field lens may not be able to provide a clear enough image to accurately determine the presence and size of the scratch.
2. Image details are not sharp enough: Although a large depth of field allows more areas to be clearly imaged, the details of the image may not be sharp enough compared to a small depth of field lens. In the detection of some of the higher requirements for edge clarity of the product, such as precision mechanical parts of the contour of the inspection, the large depth of field lens imaging of the edge may appear a little fuzzy, affecting the accuracy of the size measurement.
Effect of small depth of field on detection results

(i) Advantages
1. High-resolution imaging: Small depth-of-field lenses can focus more optical resources on a smaller depth-of-field range, resulting in higher resolution. In the scene of tiny objects or high-precision inspection requirements, the small depth of field lens can clearly capture the subtle features and defects on the surface of the object. For example, in semiconductor chip inspection, small depth of field lens can clearly distinguish the tiny lines and solder joints on the chip, and accurately detect line shorts, solder joints and other problems.
2. Highlight the focus of detection: small depth of field can make the focus of the object at the clear imaging, while the background and foreground is defocused, so that you can highlight the focus of the inspection, to avoid the interference of other irrelevant information. When detecting specific markings or tiny defects on the surface of the product, the small depth of field lens can focus attention on the parts to be detected, improving the accuracy and efficiency of the inspection. For example, in the detection of pharmaceutical packaging, the small depth of field lens can clearly present the text and patterns on the pharmaceutical packaging, making it easy to detect whether the text is clear and whether the pattern is complete.
(ii) Limitations
1. Detection range is limited: small depth of field means that only a small part of the object can be clearly imaged, which limits the scope of a detection. In the detection of larger-sized objects or the need to comprehensively detect the object surface, you may need to move the lens or adjust the focus frequently, increasing the detection time and complexity. For example, in the detection of large automotive parts, small depth of field lens may need to move several times to complete the detection of the entire surface, less efficient.
2. High requirements for the detection of the environment: small depth of field lens on the detection of the position of the object and attitude requirements are more stringent, once the object position or attitude changes, it may lead to focus shift, so that the detection area imaging fuzzy. In actual production, this requires more accurate mechanical positioning devices and stable detection environment to ensure the accuracy of detection. For example, in the detection of precision optical components, the slightest vibration or positional deviation may lead to inaccurate detection results.
How to choose the right depth of field for your inspection needs
① Detection accuracy requirements: If the detection accuracy requirements are high, such as the detection of tiny size, fine defects, etc., the small depth of field lens is more suitable, because it can provide high-resolution images to meet the demand for the capture of details. For some relatively low precision requirements, mainly focusing on the overall characteristics of the object and the approximate size of the inspection task, large depth of field lens can quickly and comprehensively complete the inspection.
② Detection of object size and shape: for large objects or irregularly shaped objects, the large depth of field lens can cover a larger range in a single imaging, reducing the detection time and operational difficulties. For small objects or objects that require precise detection of specific parts, a small depth of field lens can highlight the key points and provide clear localized images.
③ Detection environment: In the case of unstable detection environment and large fluctuations in the position of the object, the large depth-of-field lens has better adaptability; while in the case of stable detection environment and fixed position of the object, the high resolution advantage of the small depth-of-field lens can be fully utilized.
Product recommendation
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
MORE+You may also be interested in the following information
FREE CONSULTING SERVICE
Let’s help you to find the right solution for your project!


 ASK POMEAS
ASK POMEAS  PRICE INQUIRY
PRICE INQUIRY  REQUEST DEMO/TEST
REQUEST DEMO/TEST  FREE TRIAL UNIT
FREE TRIAL UNIT  ACCURATE SELECTION
ACCURATE SELECTION  ADDRESS
ADDRESS Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
