In the field of industrial manufacturing and precision inspection, tool microscope is an indispensable precision instrument. With its unique working mechanism, precise parameter setting and a wide range of application scenarios, it provides strong support for product quality control and scientific research.
Working Principle of Tool Microscope

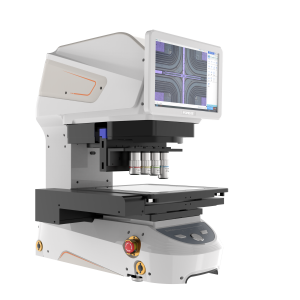
Tool microscopes work mainly on the principles of optical projection and coordinate measurement. Its optical system is similar to that of an ordinary microscope, in which the object to be measured is imaged through the objective lens and then magnified by the eyepiece for observation by the human eye. However, it is unique in that it is equipped with a high-precision coordinate measuring device. When the light shines on the measured object, the outline or details of the object are clearly imaged on the projection screen. At this point, with the help of a precisely movable table and the coordinate measuring system connected to it, the position and size of the object can be precisely measured. For example, when measuring the tooth pitch of a precision gear, the gear is placed on the table, the microscope is adjusted so that the outline of the tooth is clearly displayed on the projection screen, and then the coordinate system is used to measure the positional changes of neighboring teeth, resulting in an accurate tooth pitch value.
Tool microscope parameters
1. Measurement accuracy: This is one of the most critical parameters of a tool microscope and is usually measured in microns (μm). Common tool microscopes have a measuring accuracy of ±1μm or even higher. The high accuracy of the measurement ability to meet the high requirements for dimensional accuracy of industrial production, such as aerospace parts manufacturing and inspection.
2. Magnification: Tool microscopes generally have a magnification range of 10X - 200X. Different magnifications are suitable for different sizes of objects and different precision requirements of measurement tasks. Low magnification is suitable for observing the overall contour of larger objects, while high magnification is used for viewing minute details and making high-precision measurements.
3. Stage travel: The stage travel determines the range of object sizes that the tool microscope can measure. For example, a table travel of 200mm x 100mm in the X and Y axes means that objects with a maximum length of 200mm can be measured in the X-direction and 100mm in the Y-direction. larger table travels are suitable for measuring larger workpiece sizes.
Tool microscope applications

1、Machine manufacturing industry: In the processing of mechanical parts, tool microscope is used to detect the dimensional accuracy and shape error of parts. For example, measuring the diameter of shaft parts, cylindricity, thread pitch, tooth angle, etc., to ensure that the parts meet the design requirements, to protect the performance and reliability of mechanical equipment.
2、Electronic industry: For tiny electronic components, such as chip pin spacing, capacitance and resistance size measurement, etc., tool microscope plays an important role. Its high-precision measurement capability helps to ensure the quality and stability of electronic products and improve production efficiency.
3、Mold manufacturing: the accuracy of the mold directly affects the quality of the product. Tool microscope can be used to measure the size of the mold cavity, surface roughness, etc., to help mold makers to adjust the processing technology in time to ensure that the mold is manufactured with high precision.
4、Scientific research: In material science research, tool microscope can be used to observe the microstructure of materials, measure the size, shape and other parameters of crystals, to provide data support for the study of material properties.
Product recommendation
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
MORE+You may also be interested in the following information
FREE CONSULTING SERVICE
Let’s help you to find the right solution for your project!


 ASK POMEAS
ASK POMEAS  PRICE INQUIRY
PRICE INQUIRY  REQUEST DEMO/TEST
REQUEST DEMO/TEST  FREE TRIAL UNIT
FREE TRIAL UNIT  ACCURATE SELECTION
ACCURATE SELECTION  ADDRESS
ADDRESS Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
