Industrial camera in the machine vision system plays an important role in the transformation of optical signals into ordered electrical signals, its parameters and selection for the performance of the system is critical. The following is a detailed analysis of industrial camera parameters and selection:


Industrial camera main parameters
-
Resolution
-
Definition: The number of pixel points in a camera each time an image is captured, one of the most basic parameters of a camera.
-
Importance: Resolution directly affects the ability to show details of the image, the higher the resolution, the more obvious the display of details.
-
Common values: Common industrial face array camera resolutions are 5 million, 12 million, 65 million, etc.; line array cameras are divided by the number of pixels in the horizontal direction of the sensor, such as 2K, 4K, 8K, 16K, etc.
-
-
Pixel Depth
-
Definition: The number of bits of data per pixel, indicating the number of colors or gray levels that can be represented by each pixel point in an image.
-
Importance: The greater the pixel depth, the richer the color or gray level of the image and the greater the detail representation.
-
Common values: 8Bit, 10Bit, 12Bit, 14Bit, etc. are common.
-
-
Frame Rate/Line Rate
-
Definition: The rate at which a camera acquires transmitted images. The frame rate is the number of frames per second (fps) captured for a face array camera, and the line rate is the number of lines per second (kHz) captured by a line array camera.
-
Importance: The higher the frame rate/line frequency, the better the camera's ability to capture dynamic scenes.
-
Common values: Face array cameras have frame rates up to hundreds of fps, and line array cameras have line frequencies up to tens of kHz.
-
-
Exposure Time
-
Definition: The amount of time the shutter is open, which determines how long the camera's sensor receives light.
-
IMPORTANT: Exposure time affects the brightness and sharpness of the image and needs to be adjusted according to the lighting conditions and the target.
-
Common values: Exposure times can vary from a few microseconds to several seconds.
-
-
Pixel Size
-
Definition: the physical size of each pixel point on a camera sensor.
-
IMPORTANCE: The pixel size affects the camera's light sensitivity and image quality. In general, the larger the pixel size, the greater the light sensitivity, but the resolution may be reduced.
-
Common values: Industrial camera image element size is generally 2μm~14μm.
-
-
Spectral Range
-
Definition: the sensitivity properties of a camera sensor to different light waves.
-
Importance: Determines the spectral range that the camera is capable of capturing and is important for specific applications such as infrared detection.
-
Common values: The general response range is 350nm-1000nm.
-
-
Interface Type
-
Definition: The way the camera interfaces with external devices (e.g., image capture cards, computers).
-
Importance: The interface type affects the speed and stability of data transfer.
-
Common values: including Camera Link, GigE (Gigabit Ethernet), USB, CoaXPress, and more.
-
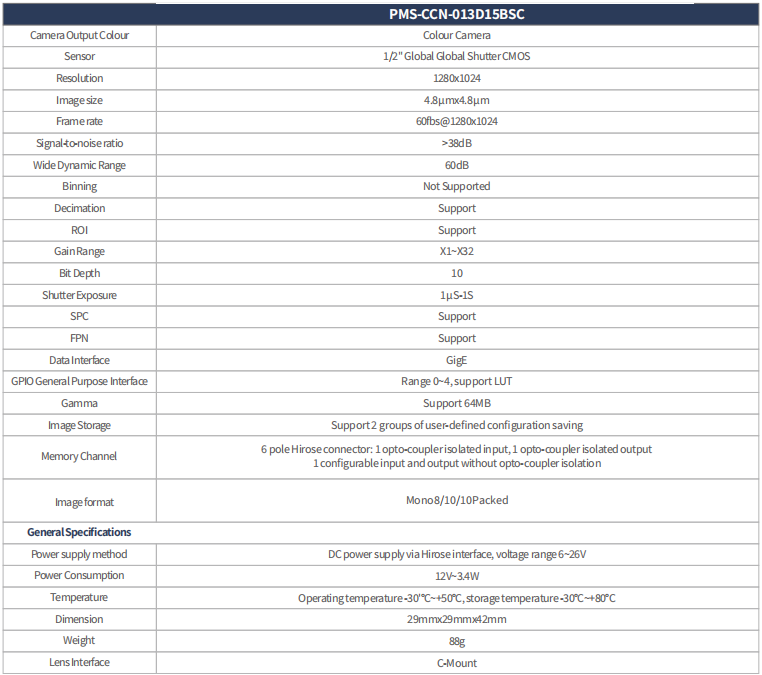
The selection of industrial cameras is a comprehensive process that takes into account a number of factors, mainly including the following aspects:
-
Project Requirements
-
Define the detection target, accuracy requirements, field of view range, etc., as a basis for selecting the appropriate camera parameters.
-
-
Camera Type
-
Choose either a face array camera or a line array camera based on the application scenario. Face array cameras are suitable for the detection of static or low-speed moving targets, while line array cameras are suitable for high-speed movement or elongated field of view.
-
-
Sensor Type
-
Choose a CCD or CMOS sensor.CCD sensors are usually superior to CMOS in terms of image quality, but CMOS sensors offer advantages in power consumption and cost.
-
-
Resolution & Pixel Depth
-
Select the appropriate resolution and pixel depth according to the detection accuracy and image quality requirements.
-
-
Frame Rate/Line Frequency
-
Select the appropriate frame rate/line frequency according to the motion speed of the detected target and the system response time requirements.
-
-
Exposure time and spectral response
-
Adjust the exposure time according to the light conditions and the characteristics of the inspection target, and consider whether special spectral response characteristics are required.
-
-
Interface Type
-
Select the appropriate interface type according to the system architecture and data transfer requirements.
-
-
Other factors
-
For example, camera durability, reliability, and maintenance costs are also factors to consider when selecting a model.
-
Founded in 2010, POMEAS is a vision technology as the core, integration of optics, control, algorithms and other technologies, focusing on the field of measurement systems, vision systems, optical systems, with customized solutions for customers to help customers improve the competitiveness of the equipment.
Product recommendation
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
MORE+You may also be interested in the following information
FREE CONSULTING SERVICE
Let’s help you to find the right solution for your project!


 ASK POMEAS
ASK POMEAS  PRICE INQUIRY
PRICE INQUIRY  REQUEST DEMO/TEST
REQUEST DEMO/TEST  FREE TRIAL UNIT
FREE TRIAL UNIT  ACCURATE SELECTION
ACCURATE SELECTION  ADDRESS
ADDRESS Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
