Effect of Depth of Field of Telecentric Lenses on Defect Detection
What is depth of field?
Depth of field is the range of object distances measured in front of a camera lens or other imager along the axis of the imager capable of achieving a clear image. Simply put, objects within this range remain relatively clear after imaging.

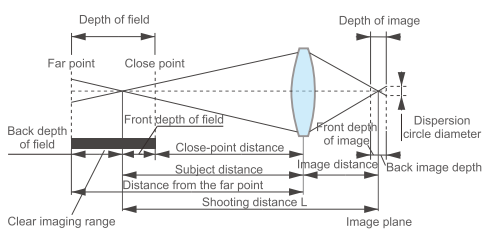
In an optical system, the size of the depth of field is affected by factors such as aperture size, focal length and shooting distance. When the aperture is smaller, the focal length is shorter and the shooting distance is moderate, the depth of field will be larger, meaning that objects with a certain distance before and after can be clearly presented in the imaging; on the contrary, when the aperture is larger, the focal length is longer, or the shooting distance is too close, the depth of field will be smaller, and only objects within a very narrow distance will be clear.

What is the impact of telecentric lens depth of field on defect detection?
1, improve detection accuracy: telecentric lens has a unique optical design, its depth of field is relatively large. In defect detection, this means that even if the surface of the object to be detected there is a certain degree of undulation or positional deviation, in the larger depth of field range, can ensure that the overall contour of the object and the characteristics of the imaging in a relatively clear. This avoids the occurrence of defects that are missed due to the blurring of part of the area caused by the shallow depth of field, which greatly improves the precision and accuracy of detection. For example, in the defect detection on the surface of electronic components, telecentric lens can be in a larger depth of field range to clearly capture the component surface of the smallest defects, whether located at the edge of the component or the center of the defects, can be accurately detected.
2, reduce focusing error: general lens in the focusing process, a slight focusing deviation may make the out-of-focus area of the object becomes blurred, thus affecting the judgment of defects. The greater depth of field characteristics of telecentric lenses, so that the operator does not need to be too precise in the detection of focus, reducing the focus inaccuracy due to misjudgment of defects in the presence or absence of the situation. In the automated defect detection system, this is particularly important to improve the stability and reliability of the detection system, reduce the downtime caused by focusing problems and adjustment time, improve the efficiency of the entire inspection program.
3, to adapt to different thickness and shape of the object: in some complex industrial inspection scenarios, the thickness and shape of the object to be detected varies. Telecentric lens with a greater depth of field can adapt to this diversity, whether it is a thin sheet of metal, thick plastic products or irregularly shaped parts, can be obtained in a shot in a clearer image, without the need to frequently adjust the parameters of the lens or re-focus for different types of objects to provide the convenience of defect detection, so that the inspection program has more versatility and flexibility.
4, reduce the environment and the location of the workpiece requirements: due to the telecentric lens depth of field is greater, the workpiece placed on the inspection platform is relatively low, unlike ordinary lenses need to be placed very accurately in a specific focus position. Even if the workpiece is slightly out of the ideal focusing position, within the depth of field of the telecentric lens, it is still possible to obtain a usable and clear image for defect detection. At the same time, in some complex industrial environments, such as the presence of vibration, unstable light and other factors, the telecentric lens depth of field can also ensure a certain degree of detection reliability, reducing the impact of environmental factors on the inspection results.
Product recommendation
TECHNICAL SOLUTION
MORE+You may also be interested in the following information
FREE CONSULTING SERVICE
Let’s help you to find the right solution for your project!


 ASK POMEAS
ASK POMEAS  PRICE INQUIRY
PRICE INQUIRY  REQUEST DEMO/TEST
REQUEST DEMO/TEST  FREE TRIAL UNIT
FREE TRIAL UNIT  ACCURATE SELECTION
ACCURATE SELECTION  ADDRESS
ADDRESS Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Tel:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867
Fax:+ 86-0769-2266 0867 E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
E-mail:marketing@pomeas.com
